Abstract
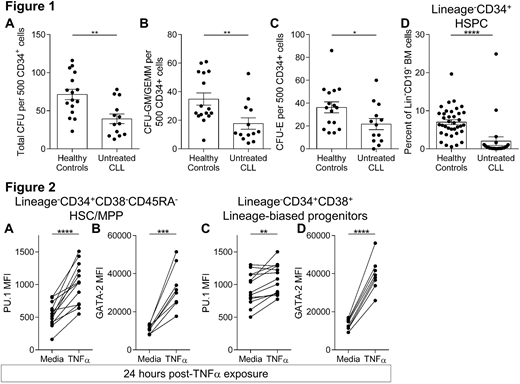
Peripheral immune dysfunction in B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is well-studied and likely relates to the incidence of serious recurrent infections and second malignancies that plague CLL patients. However, the current paradigms of known immune abnormalities are not able to consistently explain these complications and it is not easy to correct CLL patient immune status. Here, we expand on our preliminary reports that demonstrate bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic dysfunction in early and late stage untreated CLL patients. We found reduced short-term functional capacity of hematopoietic progenitors in BM using colony forming unit assays (Figure 1A-C) and flow cytometry revealed significant reductions in frequencies of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) populations (exemplified by Lin-CD34+ HSPCs, Figure 1D). We further report that protein levels of the transcriptional regulators HIF-1α, GATA-1, PU.1, and GATA-2 are overexpressed in distinct HSPC subsets from CLL patient BM, providing molecular insight into the basis of HSPC dysfunction. Interestingly, sustained myelopoiesis, evaluated by limiting dilution analysis in long-term culture-initiating cell (LTC-IC) assays maintained for five weeks, revealed no difference between healthy controls and CLL patients. These new data indicate that when HSPCs are removed from the leukemic microenvironment for ample in vitro culture time, they recover the ability to sustain myelopoiesis. To further assess the impact of the CLL microenvironment on HSPC biology, isolated HSPCs (CD34+ BM cells) from healthy controls were exposed in vitro to known leukemic microenvironment constituents. Exposure to TNFα, a cytokine constitutively produced by CLL B cells, resulted in rapid increases in PU.1 and GATA-2 proteins (Figure 2A-D). Similarly, addition of TNFα to the LTC-IC assay resulted in a striking ablation of myelopoiesis, even at the highest input cell concentration. Further, overexpression of PU.1 and GATA-2 were observed in HSPCs following co-culture with CLL B cells, a result that was not recapitulated when cells were exposed to IL-10, another cytokine constitutively produced by CLL B cells. These findings indicate specific components of the leukemic microenvironment are involved in HSPC modulation. Together, these findings expand on our previous observations of BM hematopoietic dysfunction in untreated CLL patients and offer new molecular insights into the contribution of the leukemic microenvironment on immunodeficiency in CLL.
Ding:Merck: Research Funding. Parikh:Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding. Kay:Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Acerta: Research Funding; Infinity Pharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cytomx Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal